How To Set Up Https On Wordpress
Topics
- Introduction to HTTPS for WordPress
- Implementing HTTPS for WordPress
- Best Practices for HTTPS for WordPress
- Bad Practices for HTTPS for WordPress
- References and Useful Links
Introduction to HTTPS for WordPress
To accept HTTPS, SSL Certificate is needed to be installed on the server.
Allow'south Encrypt is a not-profit organization that provides costless SSL certificates for everyone, as of Feb 2022 they have issued over 1 billion certificates. The easiest mode to get a document is to apply the EFF certbot tool, their site has consummate instructions for installing and updating certificates for several different spider web servers and operating systems.
For local development, you tin can create a self-signed certificate using OpenSSL, however this has limited utilise since any certificate generated will not be trusted by others, and then should only be used for private servers.
At that place is no actress or special settings needed specifically for WordPress at the spider web server level for HTTPS. WordPress by default is ready to use HTTPS URLs if the web server is properly configured.
The default port for HTTP URLs is port 80, the default port for HTTPS is port 443. These ports not to exist opened through whatever network firewall. Apache includes a mod_ssl module that needs to be enabled and properly configured. If using certbot, it can automatically configure and create the VirtualHost settings needed.
Tiptop ↑
Implementing HTTPS for WordPress
To implement HTTPS support on WordPress, you lot only demand to fix the WordPress and Site Accost URL to use https://. You can install WordPress either using HTTP or HTTPS to get-go, both will work, and you lot can switch over later.
Get to Settings > Full general and make sure that the WordPress Address (URL) and Site Address (URL) is https. If non, add 'Due south' after http to brand https and salvage information technology :

The Site wellness tools ( Tools >Site health) will inform you that your website doesn't use HTTPS.
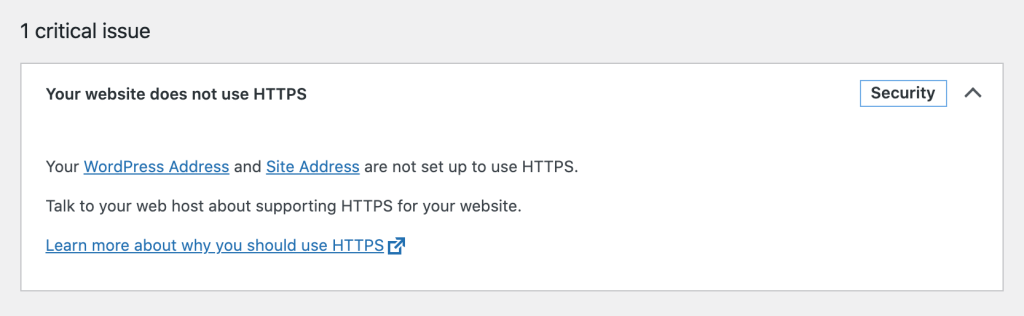
Since version five.vii, WordPress tin besides automatically switch to HTTPS if an SSL document is already set up on your server.
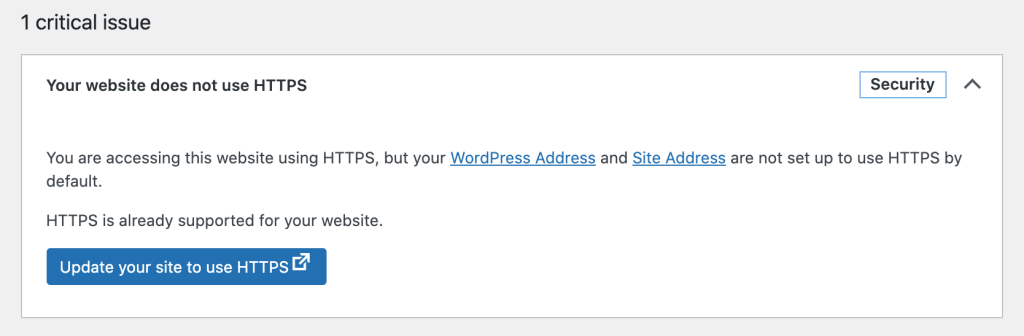
Top ↑
Best Practices for HTTPS for WordPress
It is recommended for all production WordPress sites to use HTTPS.
- Use a reputable web host, virtually provide HTTPS service as a standard.
- Use a SSL Certificate from Permit's Encrypt, they are free and easy to use.
- Serve Static Content from an SSL enabled CDN
You may demand to redirect your HTTP traffic to your HTTPS site. For Apache, you can do so by creating two VirtualHost entries for instance:
<VirtualHost *:fourscore> ServerName mkaz.blog Redirect / https://mkaz.blog/ </VirtualHost> <VirtualHost *:443> ServerName mkaz.weblog DocumentRoot /home/mkaz/sites/mkaz.blog <Directory /home/mkaz/sites/mkaz.blog> Options Indexes FollowSymLinks AllowOverride All Require all granted </Directory> SSLEngine on SSLCertificateFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/mkaz.web log/cert.pem SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/letsencrypt/alive/mkaz.blog/privkey.pem SSLCertificateChainFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/mkaz.blog/fullchain.pem IncludeOptional /etc/letsencrypt/options-ssl-apache.conf </VirtualHost> Top ↑
Bad Practices for HTTPS for WordPress
- Serving site from both HTTPS and HTTP urls, use HTTPS and redirect.
- Using mixed content, ie. CSS, JS, or images served from HTTP on an HTTPS page
Top ↑
References and Useful Links
- Why should I use HTTPS
- Let's Encrypt and Certbot
- Apache Module mod_ssl – Official Apache Module Documentation
- Encrypting the Spider web (EFF.org)
- HTTPS as a ranking signal (Google)
- Best Practices Securing Your Site (Google)
Changelog:
- Updated <date>
- <Modify>
How To Set Up Https On Wordpress,
Source: https://wordpress.org/support/article/https-for-wordpress/
Posted by: nunezbruse1960.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Set Up Https On Wordpress"
Post a Comment